In 1942, physicist Enrico Fermi and a team of workers built what they thought was the first nuclear reactor in a Chicago racket ball court. Unfortunately, nature had beaten them to the punch — by eons.
Truth be told, self-sustaining nuclear power reactor was actually invented in Africa – around 2 billion years ago! It was a 100-kilowatt nuclear plant that produced pulses of power every three hours for a period of more than 150,000 years.
The discovery of the prehistoric Oklo nuclear plant

On June 2, 1972, a French nuclear fuel reprocessing plant discovered that 200 kg of uranium had been refined from a uranium mine in the Oklo region of Gabon Republic. Fearing that someone (or a secret organization) would build a nuclear bomb, the French Atomic Energy Commission immediately opened an investigation.
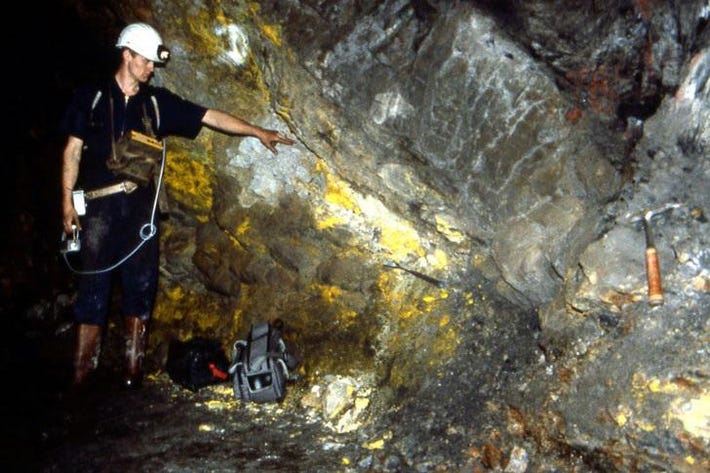

Finally, researchers and scientists from all over the world, after conducting a detailed examination, came to the conclusion that six large nuclear reactors as old as 2 billion years old are located near Gabon’s uranium mine, and has been active for at least 150,000 years!
The advanced process self-sustaining fission
The ancient nuclear reactors use surface water and groundwater to modulate and reflect sequenced fission neutrons, its operation is much more advanced than that of modern nuclear reactors. Furthermore, scientists found geological evidence that suggests uranium in lens-shaped veins of uranium ore had undergone self-sustaining fission chain reactions, generating intense heat.
In the process, subatomic neutrons released by radioactive decay of uranium atoms induce decay of other uranium atoms, leading to a cascade of nuclear fission and substantial release of energy as heat. This is what modern nuclear reactors use to produce power.
![O masini faaniukilia e 2 piliona tausaga le matutua i Aferika ua fememeaʻi ai tagata suʻesuʻe! 4 The Uranium-235 chain reaction that both leads to[-] a nuclear fission bomb, but also generates power inside a nuclear reactor, is powered by neutron absorption as its first step, resulting in the production of three additional free neutrons. E. SIEGEL, FASTFISSION / WIKIMEDIA COMMONS](https://mru.ink/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Nuclear-atomic-chain-reaction-Uranium-scaled.jpg)
The puzzle, however, is why the Oklo reactors didn’t plunge straight into a runaway chain reaction, leading to meltdown of the veins or even to an explosion. In nuclear plants the reaction is kept under control by using ‘moderators’. These are substances that either slow down the chain reaction by absorbing some of the fission neutrons or intensify it by adjusting the neutron energies.
The reactor needs pure natural water
Former head of the United States Atomic Energy Commission and Nobel laureate Dr. Glenn T. Seaborg points out: “For uranium to continue to “burn”, all conditions must be completely free of bias. The water involved in the nuclear reaction must be very pure, a few parts per million of pollutants will create a “toxic” reaction that causes the reactor to stop working. Nowhere in the world is there such pure natural water.”
The radioactive rock samples
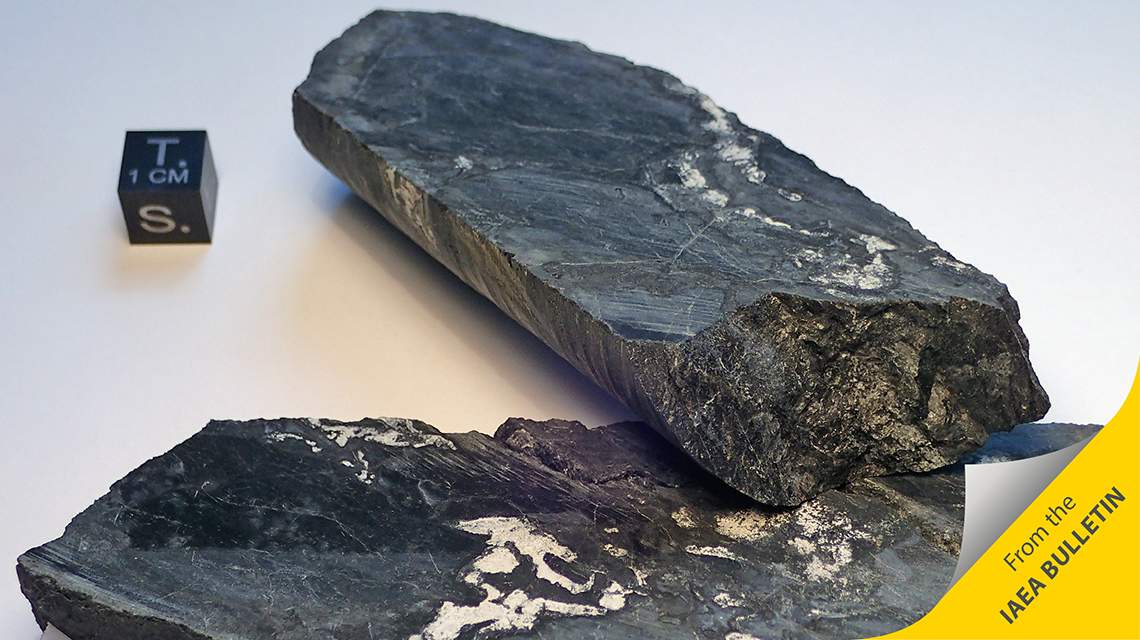

In April 2018, two rock samples recovered during drilling campaigns in Oklo were donated to the Vienna Natural History Museum. The donation (and ceremony) was made possible with funding from nuclear fuel company Orano and France’s Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA). The French Permanent Mission to the UN in Vienna supported the effort.
According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), which helped monitor radioactivity levels and handling of those samples, the two samples emit a radiation of about 40 microsieverts per hour “if you stand 5 centimetres away from them, which roughly compares to the amount of cosmic radiation a passenger would receive on an eight-hour flight from Vienna to New York.”
The incredible hypotheses
The Oklo nuclear reactor in Gabon has been operating for 1500,00 years without any interruption. How to produce water of such high purity has become another unsolved mystery. The rationality of the structural design of prehistoric nuclear reactors is absolutely baffling to experts.
A few scientists as well as some theorists believe that the reactor is extremely advanced, which suggests that 2 billion years ago highly intelligent beings existed on Earth. While another hypothesis is that it was constructed by prehistoric human civilization (like described in the Silurian Hypothesis e saienitisi NASA) using techniques that were lost to subsequent humans.

On the other side, most of the mainstream researchers have concluded saying that “Oklo is the world’s only identified naturally occurring reactor which was created by accident.” As scientists Norman Schwers and John A. Miller from Sandia National Laboratories explain in a 2017 paper, the concept of a naturally occurring reactor was originally documented in 1956 using reactor theory or the infinite multiplication constants.




